Description
Product Description
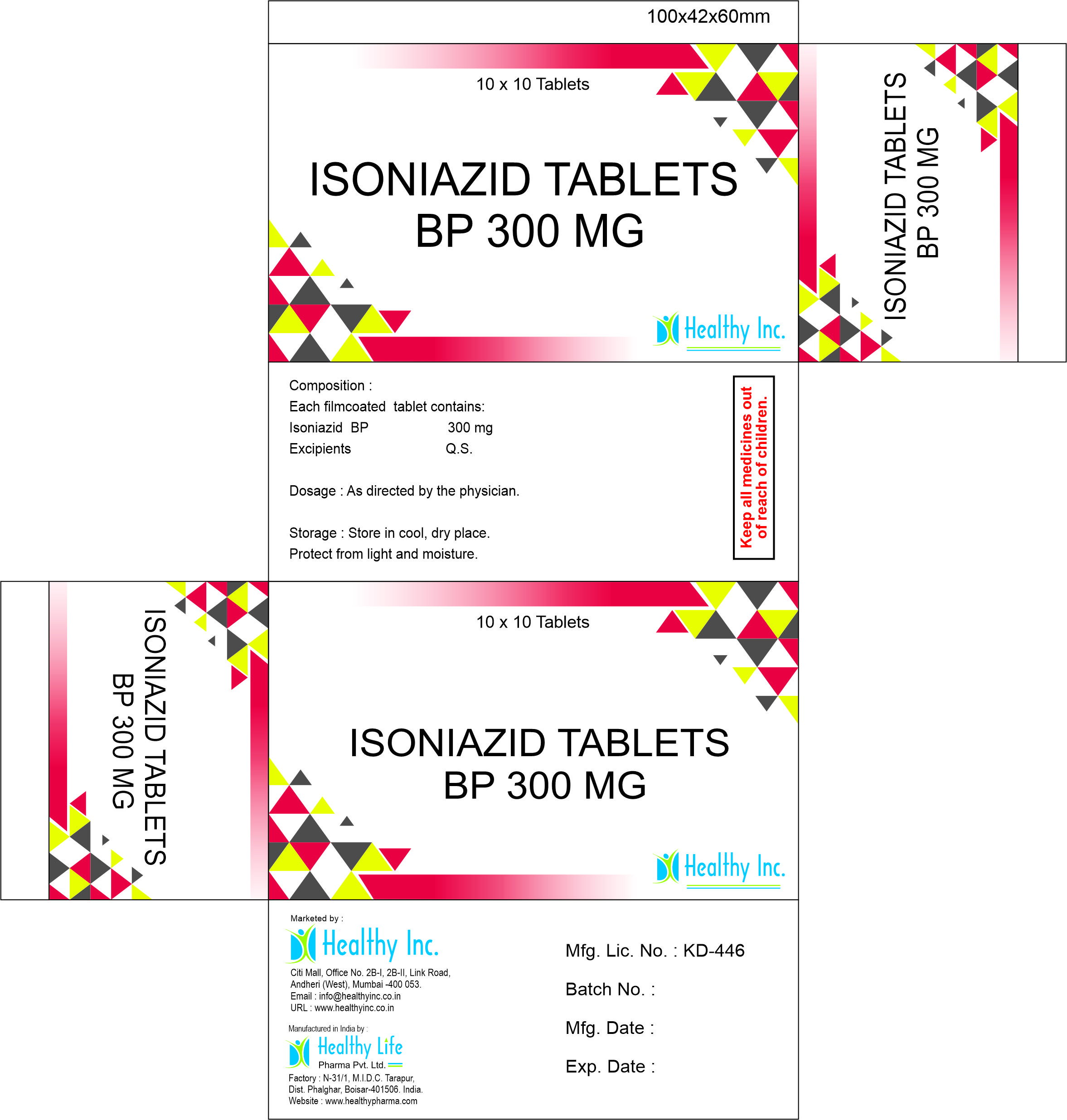
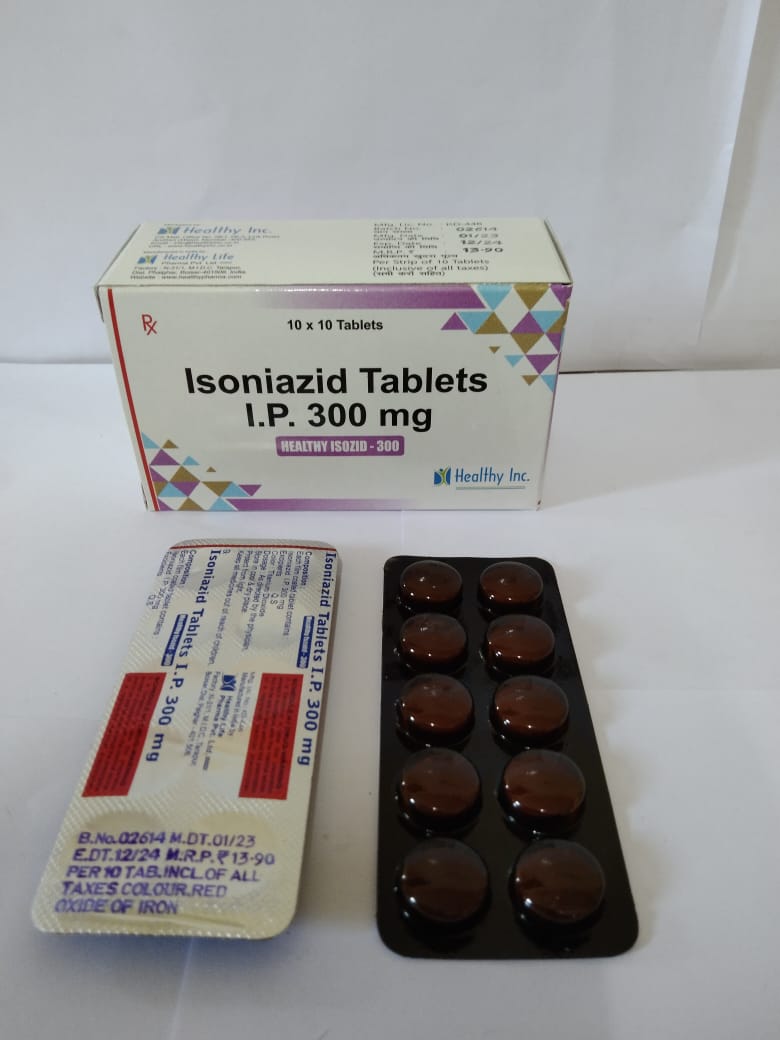
Isoniazid Tablet
Healthy Incorporation and Healthy life pharma Pvt ltd are one of the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of Isoniazid tablet 50 mg,Isoniazid tablet 100 mg,Isoniazid tablet 300 mg,Isoniazid 100 mg + Pyridoxine Hydrochloride 5 mg tablets,in India and serving the world with best quality pharmaceutical products.
Isoniazid tablet Manufacturer
Healthy incorporation and Healthy life pharma Pvt ltd, is Mumbai Based WHO GMP certified manufacturer of injection, tablets, capsules, liquid, dry syrups, pre-filled syringes, ointments etc. with an extensive experience of over 45 years in manufacturing and have reach in many countries. We are committed to provide a stock of highly effective Isoniazid tablet to our innumerable clients with the help of our well-experienced pharmaceutical specialists.
Uses of Isoniazid tablet :
Isoniazid tablets belongs to a group of medications called Antitubercular Agents. Isoniazid tablets are used with other medications to treat active TB (tuberculosis) infections. It is an antibiotic and works by preventing the growth of bacteria. It is important that you take effective and proper treatment for this condition on time.
Additional Information of Isoniazid tablet :
Product Name Isoniazid tablet
Composition & Active ingredients Isoniazid
Potency 50 mg,100 mg, 300 mg,Isoniazid 100 mg + Pyridoxine Hydrochloride 5 mg
Therapeutic use Tuberculosis
Packing 10 Tablets (1 Box)
Dosage As per Doctor Prescription
Precautions of Isoniazid tablet :
Please inform doctor your medical history of liver disease, alcohol use, HIV infection, kidney disease, diabetes,peripheral neuropathy like numbness or tingling of arms, legs, recent childbirth. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant or breast- feeding mother.
Side Effects of Isoniazid tablet :
Most of the time there is no serious side effects. Some common side effects may arise after starting medication, as your body adjust to medicine. If any of your symptoms worsen then consult your doctor immediately
Numbness or tinging in the extremities
Nausea
Loss of appetite
Vomiting
Fatigue
Weakness
Fever
Weakness
Skin rash
Stomach upset
Anxiety
Suicidal thoughts
Depression
For Detailed Product Information Contact Us at +91 7710003340, If you need Any assistance in selecting our Products that fits your requirements. If you’re looking for any product that you’re not seeing here, please contact our support team.
Isoniazid tablet
Isoniazid is an antibiotic medication that is commonly used to treat tuberculosis (TB). It is often prescribed in the form of tablets or capsules. Isoniazid works by inhibiting the growth of the bacteria responsible for tuberculosis.
Here are some key points to know about Isoniazid tablets:
Treatment of Tuberculosis: Isoniazid is a primary medication in the treatment of both latent and active tuberculosis. It is often used in combination with other antibiotics to effectively treat TB.
Latent TB: In cases of latent TB infection, where individuals are infected with the TB bacteria but do not have active disease, isoniazid is often prescribed to prevent the infection from progressing to active TB. This is known as prophylactic treatment.
Active TB: For active TB disease, isoniazid is used in combination with other anti-TB drugs to kill the bacteria causing the infection. This combination therapy is essential to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of TB.
Dosage: The dosage of isoniazid can vary depending on the specific TB treatment plan and the patient’s age and weight. It is typically taken orally as a tablet or capsule, and the medication is usually taken once daily.
Duration of Treatment: The length of treatment with isoniazid depends on the type of TB and the overall treatment plan. It can range from several months to more than a year.
Side Effects: Common side effects of isoniazid may include liver problems, peripheral neuropathy (tingling or numbness in the extremities), and gastrointestinal issues. Regular monitoring of liver function is often necessary during treatment.
Drug Interactions: Isoniazid may interact with other medications, so it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about any other drugs you are taking.
Adherence: It is crucial to take isoniazid exactly as prescribed and to complete the full course of treatment, even if you start to feel better. Stopping treatment prematurely can lead to the development of drug-resistant TB.
Precautions: Isoniazid should be used with caution in patients with liver disease and in those with a history of alcohol abuse. It is essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully.
Monitoring: While taking isoniazid, your healthcare provider may monitor your liver function through blood tests to detect any potential liver issues.
It’s important to note that isoniazid is a prescription medication, and it should only be taken under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional. If you have been prescribed isoniazid for TB or any other condition, it is crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations and report any side effects or concerns during your treatment.
Isoniazid is an antibiotic medication primarily used to treat tuberculosis (TB). It is often administered in tablet or capsule form. Isoniazid, commonly abbreviated as INH, is an essential component of the standard regimen for treating TB. It works by inhibiting the growth of the bacteria that cause tuberculosis.
Patients with active TB or those at high risk of developing TB (such as those with a positive skin or blood test for TB infection) may be prescribed isoniazid tablets as part of their treatment plan. It is typically taken once daily, and the duration of treatment can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the healthcare provider’s recommendations.
It is important to take isoniazid exactly as prescribed by a healthcare professional and to complete the entire course of treatment, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished. This is essential to ensure that the TB bacteria are completely eradicated from your body and to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
Isoniazid can have side effects, and it may interact with other medications, so it’s important to inform your healthcare provider about any other drugs or medical conditions you have before starting this medication. Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, and liver-related issues, so your doctor will monitor your liver function during treatment.
Please note that medication information can change, so it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist for the most up-to-date and specific information regarding any medication, including isoniazid tablets.
Isoniazid is a medication used to treat tuberculosis (TB) and to prevent latent TB infection from developing into active TB disease. It is an important component of combination therapy for TB. Isoniazid is typically taken as a tablet or capsule and is often combined with other anti-TB drugs to reduce the risk of drug-resistant TB.
Here are some key points about isoniazid tablets:
Usage: Isoniazid is used to treat both active TB infections and to prevent TB in individuals who have been exposed to the bacteria but have not yet developed the disease.
Dosage: The dosage of isoniazid can vary depending on the specific situation, including the patient’s age, weight, and whether they are being treated for active TB or taking it for TB prevention. It is typically taken once daily, usually on an empty stomach.
Duration of Treatment: Treatment with isoniazid can last several months or even longer, depending on the form of TB and the patient’s response to treatment. It is crucial to complete the full course of treatment to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of TB.
Side Effects: Isoniazid can have side effects, which may include nausea, vomiting, liver problems, and peripheral neuropathy (numbness and tingling in the hands and feet). Patients taking isoniazid should be monitored for these side effects.
Interaction with Food: Isoniazid should ideally be taken on an empty stomach, as taking it with certain foods, such as cheese or aged meats, can lead to an interaction known as the “cheese effect,” which can cause unpleasant symptoms like headaches and flushing.
Liver Monitoring: Patients taking isoniazid may need regular liver function tests because the drug can affect the liver. If signs of liver problems occur, the medication may need to be adjusted or stopped.
Precautions: Isoniazid should not be used by individuals with a history of severe adverse reactions to the medication or those with certain liver conditions. It should be used with caution in people who drink alcohol or have a history of substance abuse.
It’s important to note that the information provided here is general in nature, and the use of isoniazid should always be under the guidance of a healthcare professional. They can provide specific information on dosage, duration, and any potential side effects or interactions with other medications. Additionally, please keep in mind that drug information can change over time, so it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for the most up-to-date information.
Isoniazid is a medication commonly used in the treatment and prevention of tuberculosis (TB). It is available in tablet form and is often prescribed as part of a combination therapy for TB. Isoniazid works by inhibiting the growth of the bacteria that causes tuberculosis.
Here are some key points about Isoniazid tablets:
Usage: Isoniazid is primarily used to treat active tuberculosis infections. It is also used as a preventive measure in individuals who have been exposed to TB but have not yet developed the active disease.
Combination Therapy: Isoniazid is often used in combination with other anti-TB drugs, such as rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide, to increase its effectiveness and reduce the risk of drug resistance.
Dosage: The dosage of Isoniazid can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the patient’s age and weight. It is typically taken once daily on an empty stomach.
Side Effects: Common side effects of Isoniazid may include nausea, vomiting, liver problems, and peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage). It’s important to report any unusual symptoms or side effects to your healthcare provider.
Duration of Treatment: The duration of Isoniazid treatment can vary, but it is typically prescribed for several months (often at least six months) to ensure that all tuberculosis bacteria are eliminated from the body.
Preventive Use: Isoniazid is sometimes prescribed to individuals at high risk of developing active TB, such as those with close contact to a person with TB or those with a positive TB skin test. This is known as latent TB treatment.
Rifampin Interaction: Isoniazid may interact with other medications, especially rifampin. It can increase the rate at which rifampin is metabolized, so the dosages of these drugs need to be carefully managed when used together.
Liver Monitoring: Patients taking Isoniazid should have their liver function regularly monitored, as the medication can occasionally cause liver toxicity.
It’s important to take Isoniazid exactly as prescribed by a healthcare professional and to complete the full course of treatment, even if you start feeling better before the treatment is finished. This helps to prevent the development of drug-resistant TB. If you have been prescribed Isoniazid or have questions about its use, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and monitoring.
Isoniazid is a medication commonly used in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). It is usually taken orally in tablet form. Here is some essential information about Isoniazid tablets:
Purpose: Isoniazid is primarily used to treat tuberculosis, including both active and latent forms of the disease. It is often used in combination with other anti-tuberculosis drugs to effectively treat and cure TB.
Mechanism of Action: Isoniazid works by inhibiting the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria responsible for tuberculosis. It does this by interfering with the synthesis of mycolic acids, which are crucial components of the bacterial cell wall.
Dosage: The dosage of Isoniazid can vary depending on the patient’s age, weight, the severity of the TB infection, and other factors. Typically, it is taken once daily. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and the duration of treatment as directed by a healthcare provider.
Side Effects: Like any medication, Isoniazid may have side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and peripheral neuropathy (tingling or numbness in the hands or feet). In some cases, it can cause liver problems. Patients on Isoniazid are often monitored for liver function.
Drug Interactions: Isoniazid may interact with other medications, so it’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all the drugs and supplements you are taking. Some interactions can reduce the effectiveness of Isoniazid or increase the risk of side effects.
Duration of Treatment: The duration of Isoniazid treatment can vary, but it is usually taken for several months to ensure that the TB bacteria are completely eliminated. Completing the full course of treatment is essential to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of TB.
Latent TB: In some cases, Isoniazid is prescribed for individuals with latent TB infection. This is a condition in which a person has been infected with the TB bacteria but does not have active TB disease. Taking Isoniazid in these cases can help prevent the infection from becoming active.
It’s important to take Isoniazid exactly as prescribed by a healthcare professional, even if you start to feel better before the treatment is completed. Skipping doses or stopping treatment prematurely can result in the TB bacteria becoming resistant to the medication. If you have been prescribed Isoniazid or have questions about its use, please consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and monitoring.
Isoniazid is a medication commonly used to treat tuberculosis (TB) and is also sometimes prescribed as a preventive measure for those at high risk of developing active TB. It is usually taken in tablet or capsule form. Here is some basic information about Isoniazid tablets:
Active Ingredient: Isoniazid is the active ingredient in these tablets. It is an antibiotic that is effective against the bacteria responsible for tuberculosis.
Indications: Isoniazid is primarily used for the treatment of tuberculosis, both active and latent (preventing the development of active TB in individuals with latent TB infections).
Dosage: The dosage of Isoniazid can vary depending on the specific situation and the guidance of a healthcare provider. Typically, it is taken once a day, often on an empty stomach. The length of treatment can range from several months to over a year.
Adherence: It’s crucial to take the full course of Isoniazid as prescribed by a healthcare provider, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished. Failure to complete the full course can lead to drug-resistant TB.
Side Effects: Common side effects of Isoniazid may include nausea, vomiting, and neurological side effects like numbness or tingling in the extremities. It can also cause liver problems in some individuals. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is important during treatment.
Drug Interactions: Isoniazid can interact with other medications, so it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about all the drugs and supplements you are taking.
Precautions: Isoniazid should not be used by individuals with a known allergy to the drug. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider of any pre-existing medical conditions and medications you are taking to ensure its safe use.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: The use of Isoniazid during pregnancy and breastfeeding should be discussed with a healthcare provider, as the benefits and risks need to be carefully weighed.
Please note that this is general information, and the use of Isoniazid should be under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. They can provide specific information and instructions tailored to your individual circumstances.
Isoniazid is a medication primarily used to treat tuberculosis (TB). It is an antibiotic that works by inhibiting the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for TB. Isoniazid is typically taken in tablet or capsule form, and it is often used in combination with other antibiotics to treat TB effectively and reduce the risk of drug resistance.
Here are some key points about Isoniazid tablets:
Treatment of Tuberculosis: Isoniazid is a first-line treatment for both active and latent tuberculosis. In cases of active TB, it is typically used in combination with other anti-TB drugs to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
Latent TB Infection: In cases of latent TB infection (where an individual has TB bacteria in their body but is not showing symptoms), isoniazid is often prescribed to prevent the infection from progressing to active TB disease. This preventive therapy is called “latent TB treatment.”
Dosage: The dosage of isoniazid can vary depending on the specific treatment regimen and the patient’s age and weight. It is typically taken once daily, and the duration of treatment can vary from several months to more than a year, depending on the form of TB being treated.
Side Effects: Isoniazid can have side effects, and these may include liver toxicity, peripheral neuropathy, and gastrointestinal problems. Patients taking isoniazid are often monitored for these side effects, and vitamin B6 supplements are sometimes given to reduce the risk of neuropathy.
Drug Interactions: Isoniazid can interact with other medications, so it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about all the drugs you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Compliance: It’s crucial to complete the full course of isoniazid treatment as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Failing to do so can lead to treatment failure and the development of drug-resistant TB strains.
Precautions: Isoniazid may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or a history of liver disease. It’s essential to discuss your medical history and any potential concerns with your healthcare provider before starting isoniazid.
Please note that medical information can change, and it’s important to consult a healthcare professional or pharmacist for the most up-to-date and personalized information regarding the use of isoniazid or any other medication.
Isoniazid is an antibiotic medication commonly used in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB) and as a preventive measure for individuals at high risk of developing TB. It is available in tablet form and is usually taken orally.
Key information about Isoniazid tablets includes:
Purpose: Isoniazid is primarily used to treat tuberculosis (both active TB and latent TB infections). It is a crucial component of the standard TB treatment regimen.
Mechanism of Action: Isoniazid works by inhibiting the growth of the TB bacteria and preventing the spread of the infection within the body.
Dosage: The dosage of Isoniazid can vary depending on the specific TB treatment regimen, the patient’s weight, and other factors. It’s essential to take the medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Duration of Treatment: TB treatment typically involves taking Isoniazid and other antibiotics for several months (usually 6 to 9 months or longer) to ensure that the infection is completely eradicated.
Side Effects: Common side effects of Isoniazid may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and headache. In some cases, it can cause more serious side effects, such as liver toxicity or peripheral neuropathy (tingling or numbness in the hands and feet).
Precautions: Patients taking Isoniazid should avoid alcohol, as it can increase the risk of liver problems. Regular monitoring of liver function is often recommended during treatment.
Drug Interactions: Isoniazid can interact with other medications, so it’s crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking.
Adherence: It’s essential to take Isoniazid as directed by your healthcare provider and complete the full course of treatment to prevent the development of drug-resistant TB.
Latent TB: Isoniazid is also used as a preventive measure for individuals with latent TB, which means they have the TB bacteria in their bodies but are not actively sick. This preventive therapy is known as “Isoniazid preventive therapy” (IPT) and is often recommended for people at high risk of developing active TB.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, treatment, and guidance when using Isoniazid or any medication, as they can provide personalized advice based on your medical history and specific circumstances.
Isoniazid is an antibiotic medication commonly used in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). It is an essential component of first-line anti-TB therapy and is often prescribed in combination with other anti-TB drugs to effectively treat and cure TB infections. Isoniazid works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of the bacteria responsible for tuberculosis.
Here is some basic information about isoniazid tablets:
Dosage: The dosage of isoniazid can vary depending on the specific TB treatment regimen and the patient’s age and weight. It is typically taken orally, usually as a tablet or capsule. The dosage and duration of treatment will be determined by a healthcare provider.
Combination Therapy: Isoniazid is usually not used as a standalone treatment for tuberculosis. It is typically part of a combination therapy, which may also include drugs like rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. This combination helps prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of TB.
Adherence: It is crucial to take isoniazid and other TB medications exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of treatment can lead to treatment failure and the development of drug-resistant TB.
Side Effects: Like all medications, isoniazid can have side effects. Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and peripheral neuropathy (nerve problems). Less commonly, it can lead to more serious side effects, such as liver toxicity. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is necessary to catch and manage any potential side effects.
Precautions: Isoniazid may interact with other medications, and it may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as liver disease. Inform your healthcare provider of any other medications you are taking and your medical history before starting isoniazid treatment.
Duration of Treatment: The duration of isoniazid treatment can vary, but it is typically required for at least six months for active TB cases. For latent TB infection, treatment duration may be shorter. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding the duration of treatment.
It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance when taking isoniazid or any other prescription medication, especially for a serious condition like tuberculosis. If you have been prescribed isoniazid or have questions about its use, make sure to discuss your concerns and any potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
Isoniazid is an antibiotic medication used primarily in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB) and, to a lesser extent, for the prevention of TB infection. It is commonly administered in tablet or capsule form and is usually taken orally. Isoniazid works by inhibiting the growth of the tuberculosis bacteria, which helps to treat and prevent the spread of the disease.
Here are some key points to keep in mind about Isoniazid tablets:
Indications: Isoniazid is mainly used to treat active tuberculosis (TB) and to prevent TB in individuals who have been exposed to the disease. It is often prescribed in combination with other TB medications to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
Dosage: The dosage of Isoniazid can vary depending on the individual, the specific TB regimen, and the form of TB being treated. It’s important to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment as directed by a healthcare professional.
Side Effects: Common side effects of Isoniazid may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and numbness or tingling in the hands or feet. Some people may experience more serious side effects, such as liver problems. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is often necessary during treatment.
Precautions: It’s important to inform your healthcare provider of any pre-existing medical conditions or medications you may be taking, as Isoniazid can interact with other drugs and may not be suitable for everyone.
Duration of Treatment: Treatment with Isoniazid and other anti-TB drugs typically lasts for several months to ensure the complete eradication of the bacteria. It is crucial to complete the entire course of treatment, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the development of drug-resistant TB.
Tuberculosis Control: Isoniazid is a critical component of tuberculosis control programs worldwide, helping to reduce the incidence and prevalence of TB.
Isoniazid should only be used under the guidance and supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. If you have been prescribed Isoniazid or have questions about its use, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and instructions.
Note: Healthy Incorporation and Healthy life pharma Pvt ltd tries to ensure that all information, whether in relation to the products, services, offerings provided as part of this website is correct at the time of inclusion on the website, Unauthorized use of any materials contained on this website may violate copyright laws, trademark laws, the laws of privacy and publicity, certain communications statutes and regulations and other applicable laws and regulations. All copyright and other intellectual property rights in this material are owned by Healthy Incorporation and Healthy life pharma Pvt ltd. Please connect with us to discuss precise product specifications and requirements and obtain advice on which products are suitable for your requirement or you can write to us
Isoniazid Tablet , आइसोनियाज़िड टैबलेट एमजीएमजीएमजी ,Isoniazida Comprimido , Comprimé d’isoniazide , أيزونيازيد أقراص ملجم ملجم ملجم , 異煙肼片 , Comprimido de isoniazida , Изониазид таблетка , イソニアジド錠 , suppliers India, Exporters, Wholesalers India, Distributors India, Generic Supplier,who gmp certified manufacturer